Test Owner
SAP customers question ROI of S/4HANA shift
Many SAP customers remain unconvinced about the business case for moving from perpetual licenses to SAP’s subscription-based S/4HANA cloud platform, as concerns grow over rising costs and uncertain returns on investment.
SAP is set to end mainstream support for its legacy ECC ERP system at the end of this year, with extended maintenance options available until 2030. While the company is encouraging customers to migrate to S/4HANA Cloud, adoption has been slower than expected, largely due to pricing concerns and the effort required to justify the upgrade.
A recent survey of SAP users found that the vast majority are worried about unpredictable subscription price increases over time. Most respondents also said building a clear return-on-investment case for S/4HANA is either difficult or requires significant effort. Many believe the software they already run has a longer useful life than SAP’s support timelines suggest.
As a result, a significant share of customers say they do not expect to be running S/4HANA in the cloud within the next five years, with some planning to remain on on-premises ECC systems for as long as possible. Customers cite loss of control and reduced flexibility as key drawbacks of moving away from perpetual licensing.
Despite customer hesitation, SAP reports strong growth in cloud ERP revenue, pointing to increasing adoption of its core cloud offerings. The company maintains that customers are migrating at scale, even as a sizeable ECC user base remains undecided.
The debate is less about software quality than strategy. Many customers still view SAP’s ERP as robust and difficult to replace, but increasingly question the value of large, all-in-one platforms. Instead, many expect to pursue a more modular ERP approach in the future, combining systems from multiple vendors to meet specific needs.
Even so, most customers are not abandoning SAP altogether. While some are evaluating alternatives or extended ECC support, many are taking a cautious, wait-and-see approach—assessing migration options within the SAP ecosystem and hoping for further flexibility on support deadlines as they plan their next steps.
The SAP Contracting Market in Hungary in 2026
In 2026, the SAP contracting market in Hungary is defined by sustained, high demand driven by mandatory digital transformation programs—most notably the large-scale migration of enterprise systems to SAP S/4HANA. As organizations modernize legacy SAP environments, Budapest has firmly established itself as a key European hub for SAP talent, combining competitive contractor rates with a rapidly expanding ecosystem of local and international consultancies.
Market Dynamics and Demand
Primary Demand Drivers
The Hungarian SAP market is being reshaped by the accelerated adoption of cloud-based ERP solutions, including SAP S/4HANA Public and Private Editions. Alongside core migrations, companies are increasingly integrating AI, analytics, and process automation into their SAP landscapes to improve efficiency, compliance, and decision-making.
High-Demand SAP Skills
There is particularly strong demand for experienced specialists in:
SAP MM (Materials Management)
SAP SD (Sales and Distribution)
SAP FI/CO (Finance and Controlling)
End-to-end SAP S/4HANA transformation expertise
Professionals who combine functional knowledge with technical S/4HANA migration experience are especially sought after.
Key Industry Sectors
Manufacturing, financial services, and logistics remain the dominant sectors for SAP implementations and upgrades in Hungary. These industries are under pressure to modernize core systems while maintaining operational continuity, which continues to fuel demand for external SAP contractors.
Rates, Salaries, and Talent Availability
Contractor Rates
SAP freelancers operating in Hungary typically command daily rates between HUF 100,000 and HUF 200,000 (€260–€520), depending on specialization, project complexity, and language requirements.
Permanent Compensation
For permanent roles, SAP management consultants earn average annual salaries of approximately HUF 10.41 million to HUF 11.54 million or more as of early 2026, reflecting steady upward pressure on compensation.
Talent Shortage
The market remains structurally tight. Around 47% of companies report a shortage of SAP professionals, creating a highly competitive hiring environment. As a result, an estimated 55% of SAP specialists are open to changing roles for higher pay, more flexible working conditions, or clearer career progression.
Key Considerations for SAP Contractors
Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
All SAP contractors and consulting firms must comply with EU-wide data protection rules, including GDPR, which is mandatory for projects involving personal or sensitive business data.
Regional Demand Beyond Budapest
While Budapest remains the primary SAP hub, growing demand can also be found in other industrial and academic centers such as Debrecen, Miskolc, and Győr, particularly where manufacturing and shared service centers are concentrated.
Workplace and Delivery Models
Hybrid and remote work models have become the norm for many SAP projects. However, certain high-impact roles—especially during critical project phases such as go-lives—may still require occasional on-site presence.
Resources for Finding SAP Contract Roles
Recruitment Agencies
Specialized recruiters such as Inter-Consulting Europe (UK) Ltd are actively placing SAP contractors in the Hungarian market.
Consulting and Implementation Partners
Large-scale SAP programs are commonly led by established consultancies including Deloitte Hungary, Kontron Hungary, and BCS Consult, all of which maintain a strong local presence.
PTC’s Windchill has solidified its position as one of the most advanced and widely adopted Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) platforms on the market. As global industries increasingly embrace digital transformation, PTC is experiencing significant growth driven by strategic investments, technology innovation, and expanding market demand for connected, cloud-based PLM solutions.
Market Performance and Financial Indicators
Robust financial results underline PTC’s momentum.
In fiscal year 2024, PTC reported a 12% increase in constant currency Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR), underscoring the company’s ability to sustain double-digit growth in a competitive software landscape. For fiscal year 2025, PTC projects ARR growth of 9% to 10%, signaling continued confidence in its recurring revenue model.
The company’s Q4 2024 results showed a 14.62% year-over-year revenue increase, demonstrating resilience and expansion even amid macroeconomic headwinds. Market analysts have echoed this optimism: in February 2024, Seeking Alpha issued a “Buy” rating for PTC, projecting low-teens growth over the next three fiscal years.
PTC’s acquisition strategy also continues to bear fruit. The integration of ServiceMax—a leader in field service management—has opened up new cross-selling opportunities and expanded PTC’s footprint in adjacent digital transformation markets.
Strategic Growth Drivers
1. Integration with AI, IoT, and AR
PTC is advancing Windchill’s capabilities through the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), industrial Internet of Things (IoT), and augmented reality (AR).
In March 2025, PTC announced plans to showcase “Windchill AI” at Hannover Messe, highlighting AI-driven “digital thread” solutions developed in partnership with Microsoft. These innovations strengthen PTC’s value proposition by enabling predictive analytics, smarter design workflows, and real-time collaboration across engineering and manufacturing operations.
2. Cloud and SaaS Transformation
The global shift toward cloud-based PLM has been a major growth catalyst. PTC offers Windchill both on-premise and as a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), aligning perfectly with customer demand for scalable, flexible deployment options.
Industry data shows the SaaS PLM segment accounted for more than 74% of total PLM revenue in 2022, a figure expected to grow as manufacturers modernize their digital infrastructure.
3. Industry Leadership Recognition
PTC’s leadership in the PLM space continues to receive third-party validation.
ABI Research (2024) named PTC the “outright leading vendor” in its Competitive Assessment for Enterprise PLM in large manufacturing organizations.
Quadrant Knowledge Solutions (2023) recognized PTC as the technology leader in its SPARK Matrix for the global PLM market.
4. Strategic Partnerships
Collaborations with global technology giants such as Microsoft and Amazon Web Services (AWS) amplify Windchill’s reach and capabilities. These partnerships enable deeper integration with cloud, AI, and IoT ecosystems, giving customers a unified digital platform for end-to-end product lifecycle management.
Competitive Landscape and Market Position
PTC operates in a highly competitive environment alongside major players such as Dassault Systèmes (SOLIDWORKS, 3DEXPERIENCE) and Siemens (Teamcenter).
However, according to Enlyft data (2025), PTC Windchill maintains a strong market share, particularly within industries that demand high levels of product complexity and regulatory compliance.
Windchill is widely adopted in automotive, aerospace and defense, and industrial machinery, where digital continuity and collaboration are mission-critical. Automotive OEMs, in particular, have accelerated adoption as they move toward electrification and smart manufacturing.
Risks to Future Growth
Despite its strong position, PTC faces several challenges that could impact growth:
Macroeconomic headwinds may influence enterprise spending, leading to delayed purchasing decisions or elongated sales cycles.
Intensifying competition from Dassault, Siemens, and emerging PLM vendors means PTC must continue to innovate and invest in differentiated technologies.
High valuation expectations present a financial risk. According to InvestingPro, PTC trades at a premium earnings multiple, implying strong investor confidence—but also little room for missed targets.
In today’s rapidly evolving business environment, medium-sized companies are under growing pressure to operate with the same agility, accuracy, and visibility as large enterprises — but often with leaner teams and tighter budgets. As a result, many are turning to modern enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms to gain a competitive edge, streamline operations, and position themselves for growth. One of the most trusted players in this space is Microsoft Dynamics 365, which has steadily expanded its market share thanks to its modular, cloud-based architecture and its ability to scale with a business’s needs.
The global ERP market is experiencing consistent growth, driven largely by digital transformation initiatives among mid-market companies. A few key trends stand out:
Cloud ERP adoption is accelerating, with more businesses moving away from legacy on-premises systems.
Mid-sized businesses account for a growing share of ERP investments, as they seek to modernize operations.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 has emerged as a leading solution in this space, thanks to its flexible deployment, integration capabilities, and strong ecosystem.
Medium-sized companies typically require robust tools but can’t always afford the heavy infrastructure and customization costs associated with enterprise-level solutions. This is where modern, cloud-based ERP platformsprovide exceptional value.
Why Medium-Sized Companies Prefer ERP
1. End-to-End Visibility Across the Business
Growing businesses often rely on multiple disconnected systems — for accounting, inventory, sales, and customer management. ERP consolidates these functions into one centralized platform.
With Dynamics 365, companies get real-time access to financial data, supply chain information, sales performance, and workforce analytics — all in one place. This level of visibility improves decision-making, forecasting, and operational control.
2. Scalability Without Complexity
Medium-sized businesses need solutions that can grow with them. Unlike rigid legacy systems, modern ERPs like Dynamics 365 offer modular functionality. Companies can start with core financials and operations, then easily add modules such as supply chain management, HR, or project operations as their business evolves.
This means no expensive rip-and-replace projects — just seamless growth.
3. Lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Cloud ERP eliminates the need for expensive hardware, servers, and in-house IT teams to manage infrastructure. With subscription-based pricing, medium-sized companies pay for what they need, when they need it, keeping costs predictable and manageable.
4. Automation & Efficiency
Manual processes slow companies down. ERP automates routine tasks — from invoice processing and inventory updates to payroll and reporting. This frees up teams to focus on strategy and growth rather than administrative work.
Dynamics 365’s AI-driven insights and automated workflows help medium-sized organizations achieve enterprise-level efficiency without enterprise-level overhead.
5. Integration & Flexibility
Medium-sized companies often use multiple tools, such as CRM systems, e-commerce platforms, or HR software. Dynamics 365 integrates natively with Microsoft 365, Power BI, and third-party applications.
This interconnectivity reduces silos, enhances collaboration, and improves reporting accuracy.
6. Security & Compliance
Data security is critical for growing businesses. Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure provides enterprise-grade security, compliance with international standards, and reliable uptime. This allows mid-sized companies to enjoy the same level of protection as global corporations — without needing a dedicated security team.
Dynamics 365 ERP Modules for Medium-Sized Companies
Dynamics 365 offers several ERP applications tailored to different business needs:
Dynamics 365 Business Central – Ideal for SMBs, covering finance, operations, sales, and customer service.
Dynamics 365 Finance – Advanced financial reporting, budgeting, and global consolidation.
Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management – Streamlining manufacturing, inventory, and logistics.
Dynamics 365 Commerce – Omnichannel retail and e-commerce.
Dynamics 365 Project Operations – Project-based business management.
Dynamics 365 Human Resources – Comprehensive HR management.
Dynamics 365 Intelligent Order Management – Automating and managing order fulfillment.
For companies currently running legacy on-premises systems like Dynamics NAV or Dynamics GP, migrating to the cloud unlocks new capabilities and long-term cost savings.
To conclude, the ERP market is no longer dominated only by large corporations. Medium-sized companies are adopting ERP at record speed, leveraging the flexibility and affordability of modern cloud solutions like Dynamics 365. By centralizing business operations, improving efficiency, and enabling smarter decision-making, ERP systems empower mid-market organizations to compete on a global scale — without the complexity and cost of traditional enterprise IT.
The Language That Won’t Die
In an industry obsessed with the next big thing, few technologies have the endurance of COBOL. Born in 1959, COBOL (Common Business-Oriented Language) predates the internet, personal computers, and even the moon landing. And yet, it continues to power much of the world’s critical infrastructure. From banking networks and insurance claims to healthcare billing and government benefits, COBOL is not a relic—it’s a backbone. Quietly, it processes the world’s most sensitive and high-volume workloads every single day. The question isn’t why COBOL is still here. It’s why it continues to thrive—and what that means for your IT roadmap.
The Numbers Behind COBOL’s Endurance
The scale of COBOL in today’s economy is hard to ignore:
220+ billion lines of active COBOL code worldwide.
70–80% of business transactions touch COBOL at some point.
30+ billion COBOL transactions are processed every single day.
This isn’t forgotten legacy code sitting on a shelf—it’s mission-critical infrastructure. The systems that move money, settle insurance claims, process hospital records, and run manufacturing lines are still overwhelmingly written in COBOL. Why? Because replacing them isn’t simply “upgrading code.” It’s rewriting decades of embedded business rules, passing regulatory audits, retraining staff, and absorbing enormous operational risk. In a world chasing agility, COBOL survives because it delivers something rarer: predictability at scale.
Why Enterprises Still Rely on COBOL
Stability Over Novelty
COBOL systems have decades of uptime behind them. They run 24/7 with minimal failure—vital in industries where outages mean lost revenue, fines, or risks to public safety.Deep Integration
Banking settlements, claims adjudication, and logistics tracking all depend on COBOL’s tight coupling with mainframes, schedulers, and databases. Pull one piece out, and the entire workflow can collapse.The Cost Equation
A full rewrite can run into the tens of millions. Add downtime, retraining, and compliance hurdles, and the ROI is rarely favorable.Regulatory Entrenchment
COBOL systems are certified and audit-proven. Replacing them often means reopening compliance processes—a nightmare for industries like finance and healthcare.Institutional Knowledge in Code
COBOL systems encode decades of business rules, often undocumented. Replacing them means relearning your business logic from scratch—a task more cultural than technical.
Simply put: COBOL isn’t hanging on despite its age. It’s thriving because, for certain workloads, it remains the lowest-risk option available.
Where COBOL Still Reigns Supreme
Banking & Financial Services
Powers core banking, ATM networks, fraud detection, and payment rails. North American banks alone spend $11.8B annually modernizing COBOL systems.Healthcare & Insurance
Manages eligibility checks, billing, and public health programs. California’s Medi-Cal committed $220M to modernize its COBOL-based eligibility engine.Manufacturing
Runs legacy MRP systems and even production-line controllers. Modernizing a single plant line can cost $850K–$4.2M, so gradual upgrades are the norm.Government
Tax processing, unemployment benefits, and defense logistics all lean on COBOL. The U.S. GAO flagged 10 federal systems still running COBOL, costing $337M annually in upkeep.
These industries aren’t behind—they’re risk-aware. For them, COBOL is not a weakness. It’s a strategic safeguard.
The Real Risk: People, Not Code
COBOL itself works just fine. The real problem is the human layer.
The Retirement Cliff – Nearly 70% of COBOL programmers are due to retire by 2025.
Knowledge Loss – Decades of undocumented business rules risk disappearing with them.
Talent Gap – Universities don’t teach COBOL, and younger developers avoid it, citing outdated tools and limited career prospects.
This creates “human technical debt.” Even bulletproof systems become fragile if no one can maintain them. That fragility is already surfacing: during the COVID-19 crisis, some U.S. states publicly begged for COBOL programmers to keep unemployment systems afloat.
What This Means for Your IT Strategy
COBOL isn’t going anywhere soon—but your strategy around it must evolve. CIOs and CTOs face a clear challenge: how to modernize without destabilizing mission-critical systems.
Here’s the path forward:
1. Stabilize the Present
Audit COBOL systems
Automate documentation
Build failover protocols
Create knowledge-transfer programs before retirements hit
2. Build a Skills Bridge
Pair senior COBOL experts with younger developers
Incentivize COBOL upskilling internally
Use AI-powered assistants to accelerate onboarding and reduce dependency on shrinking expertise
3. Wrap, Don’t Replace
Use APIs and middleware to expose COBOL functions to modern systems
Integrate with mobile apps, cloud analytics, and AI without touching the core logic
4. Refactor Strategically
Selectively modernize high-change areas like reporting or customer interfaces
Extract business rules into decision engines for reuse in modern applications
5. Leverage AI and Emulation
Use AI-driven code converters to assist migration (with strict validation)
Run COBOL in containers or emulators for cloud flexibility and reduced mainframe dependency
What is RISE with SAP – And Why It Matters
For years, SAP has been the trusted backbone of enterprise operations, running mission-critical processes for companies like Unilever, Siemens, and Mercedes-Benz. But the way businesses consume technology is changing — and so is SAP.
With RISE with SAP, the company is offering a new approach: a single, subscription-based package that bundles everything a business needs to migrate to the cloud, modernize operations, and become what SAP calls an “intelligent enterprise.”
From On-Premise to the Cloud — Without the Headaches
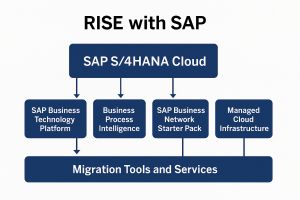
Traditionally, moving from SAP ECC (or any legacy ERP) to the next-generation S/4HANA required multiple vendors, separate infrastructure contracts, and a significant IT coordination effort. RISE with SAP simplifies this by combining:
SAP S/4HANA Cloud – the digital core, available in a private edition (for tailored migrations) or public edition (for standardized, fast deployments).
SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) – credits for building custom apps, integrations, and AI-driven workflows.
Business Process Intelligence (powered by SAP Signavio) – tools that let businesses map their processes, find inefficiencies, and benchmark against industry best practices.
SAP Business Network Starter Pack – access to SAP’s procurement, logistics, and asset intelligence networks for better supplier collaboration.
Managed Cloud Infrastructure – hosted on hyperscalers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud, with SAP managing the operations.
Migration Tools and Services – using SAP Activate methodology to guide businesses step by step.
In short, RISE with SAP removes much of the complexity of digital transformation by putting software, infrastructure, and services under a single contract — with SAP as the accountable partner.
Why Companies Are Signing On
Enterprises across industries are seeing the benefits. Microsoft migrated some of its internal finance systems to S/4HANA in the cloud. Coca-Cola İçecek, one of the world’s largest Coca-Cola bottlers, used RISE with SAP to streamline operations across 11 countries. Even smaller manufacturers are leveraging it to scale faster and access technologies like AI-driven demand forecasting and predictive maintenance.
The key benefits often cited include:
Simplification – no more managing multiple vendors or data center operations.
Speed & Innovation – regular updates and faster access to features like embedded analytics, machine learning, and automation.
Agility – the ability to pivot operations quickly, whether scaling production or entering new markets.
Cost Predictability – moving from capital-heavy IT investments to a predictable subscription model.
Data-Driven Process Optimization – using Signavio insights to redesign processes for efficiency.
The Bigger Picture
RISE with SAP is more than a product bundle — it’s SAP’s strategy to keep its vast customer base engaged as the software world shifts to the cloud. Competitors like Oracle NetSuite, Infor, and Microsoft Dynamics 365 are chasing the same enterprise customers with cloud-first solutions.
By offering RISE, SAP positions itself not just as a software vendor but as a transformation partner. For companies facing pressure to modernize quickly — whether due to supply chain disruption, rising costs, or global competition — RISE provides a curated, lower-risk path to get there.
The SAP S/4HANA migration market is one of the fastest-growing segments in enterprise software today. With the 2027 deadline for SAP ECC’s mainstream maintenance looming, companies across industries are racing to modernize their ERP systems. This rush is fueling not only a massive technology shift but also an unprecedented demand for skilled SAP consultants, cloud migration experts, and ERP project managers.
Market Size and Growth
The numbers behind the S/4HANA market are striking. Analysts estimate the 2024 market size for SAP S/4HANA applications at $5.2 billion to $26.3 billion, depending on whether you include surrounding services such as implementation, training, and managed support.
Looking ahead, the market shows no signs of slowing down:
$16 billion by 2033 – projected value for the core S/4HANA application market.
$60+ billion by 2030 – when including SAP HANA and the full ecosystem of partners, services, and integrations.
This growth is not just about software licenses — it’s about a full-scale transformation of enterprise operations worldwide.
The Migration Wave
At the heart of this market boom is the mass migration of roughly 30,000 SAP ECC customers who must convert to S/4HANA before 2027. This migration wave represents one of the largest coordinated IT shifts in history, creating a surge in:
Implementation projects – large-scale rollouts of new ERP systems.
Consulting opportunities – guiding enterprises through process redesign and change management.
Cloud adoption – many organizations are using this transition to move to SAP S/4HANA Cloud or hyperscaler platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Adoption Trends & Real-World Examples
As of mid-2025, 28,000+ companies are running S/4HANA — and the list includes some of the biggest names in global business:
Walmart – modernizing finance and supply chain management with S/4HANA.
Amazon – leveraging S/4HANA for global inventory and logistics optimization.
Apple – streamlining manufacturing operations and financial consolidation.
Siemens, Nestlé, Unilever – investing in long-term ERP transformation roadmaps.
Even with these headline-grabbing projects, only 37% of SAP customers worldwide had purchased S/4HANA licenses by 2024, meaning most migrations are still ahead. Adoption is highest in IT & Services (22%) and Software (6%), with the U.S., India, and Germany leading the charge geographically.
Competitive Landscape
SAP S/4HANA commands about 10.19% of the global ERP market, putting it in fierce competition with Microsoft Dynamics 365, Workday, and Oracle NetSuite. Beyond the core software, a vast $89+ billion services market has emerged for S/4HANA implementations, upgrades, and ongoing support. Key players — including Deloitte, Capgemini, Accenture, and SAP’s own consulting arm — are scaling their teams and hiring aggressively to meet surging client demand.
Bottom Line
The S/4HANA migration market in 2025 is not just large — it’s accelerating. With less than two years left before ECC support ends, thousands of enterprises still need to migrate. For SAP customers, this is a crucial moment to lock in roadmaps and resources. For technology professionals, integrators, and consultants, the opportunity is enormous — offering years of project work and career growth in one of the most significant enterprise IT transitions of the decade.
As of early September 2025, SAP has doubled down on artificial intelligence, sovereign cloud services, and high-profile acquisitions in an effort to strengthen its position as a global enterprise software leader. The company’s latest announcements highlight its ambition to combine innovation with digital sovereignty, while addressing ongoing customer concerns about cloud migration.
Driving AI Innovation
SAP’s generative AI copilot, Joule, is expanding rapidly across its business application portfolio. The newest updates introduce AI agents for supply chain, finance, and procurement, while also embedding Joule into Microsoft Teams and Microsoft 365 Copilot. These integrations aim to streamline workflows and enhance everyday productivity for users.
For developers, SAP is enhancing its Business Technology Platform (BTP) with AI-assisted tools. Additions to SAP Build and SAP HANA Cloud are designed to simplify the creation of custom AI applications and strengthen data integration, giving development teams more flexibility and speed.
Reinforcing Cloud and Data Sovereignty
A central theme of SAP’s strategy is sovereign cloud expansion in Europe. The company announced an investment of over €20 billion to boost digital independence and foster AI innovation in the region.
SAP also unveiled a new “Sovereign Cloud On-Site” service, enabling customers to run cloud workloads directly in their own data centers. Managed by SAP-certified staff, this offering promises greater control, compliance, and data sovereignty.
At the same time, SAP continues to push its S/4HANA Cloud migration agenda. While customers have been given more time to transition from on-premise solutions, challenges around costs, complexity, and readiness persist.
Expanding Through Acquisitions and Partnerships
In August, SAP confirmed plans to acquire SmartRecruiters, an AI-driven talent acquisition platform. The move will strengthen SAP SuccessFactors HCM by enhancing recruiting and hiring capabilities.
SAP is also entering the fast lane with a partnership with the Mercedes-AMG PETRONAS Formula 1 team, which will leverage SAP’s Cloud ERP to improve performance and data-driven decision-making.
Other recent collaborations include:
Alibaba – hosting SAP cloud workloads in China
AWS and NVIDIA – joint initiatives to accelerate enterprise AI adoption
Other Key Developments
Maintenance Fee Adjustments: Beginning January 1, 2026, SAP will link support contract fees to the Consumer Price Index (CPI), with a maximum annual increase of 5%.
Security Updates: In August, SAP released patches for several critical vulnerabilities, including high-severity issues affecting its Graphical User Interface (GUI).
Customer Sentiment: Despite SAP’s AI and cloud-first vision, many customers remain cautious. Concerns center on pricing transparency, migration difficulties with RISE, and reduced focus on on-premise solutions.
SAP CEO Christian Klein believes Europe should avoid replicating the U.S.’s large-scale AI infrastructure expansion. In his view, a European version of the massive “Stargate” initiative wouldn't offer as much value as focusing on the practical deployment of AI in key industries.
Klein shared his thoughts during a recent media interview, responding to European proposals to build five AI “gigafactories.” These large data centers, which many cities are now competing to host, aim to bolster the continent's AI capabilities. But Klein remains unconvinced that this kind of buildout is necessary.
The Commoditization of AI Models
Klein argues that large language models (LLMs), despite their high training demands, are rapidly becoming commoditized. He cites the surprising success of Chinese company DeepSeek, which launched a model that rivals offerings from OpenAI and Google — and did so without massive infrastructure.
Instead of matching U.S. spending, Klein suggests that Europe should focus on industry-specific AI applications, particularly in sectors like automotive and chemicals. According to him, targeted innovation would deliver far more value than building an expensive AI superstructure.
Fragmented Progress Already Underway
This approach is already taking root across Europe, though in a fragmented way. For example:
Juvoly is advancing AI speech recognition in Dutch.
Silo AI, a Finnish company recently acquired by AMD, is building multilingual LLMs for the Nordic region.
Cradle, a startup in the biotech space, is developing tools to make biology programmable through AI.
However, in the automotive sector — a priority area for Klein — Europe appears to be falling behind. Klein may well prefer to see the EU’s €20 billion AI infrastructure fund redirected toward innovations in battery technology or autonomous vehicles, though these are also areas where Europe is struggling to keep pace.
The Investment Gap Is Stark
The contrast in ambition between Europe and the U.S. is hard to ignore. American tech giants have laid out plans to spend up to $500 billion on the “Stargate” project alone. Meanwhile, Europe’s commitment stands at just €20 billion for its proposed five AI centers — a 20-fold difference.
This gap was highlighted again during Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang’s recent visit to Europe. Huang warned that Europe’s AI progress is being throttled by limited computing power and announced plans to expand Nvidia’s hardware footprint across the continent. Naturally, Nvidia stands to benefit from such expansion — the demand for GPUs, the "pickaxes" of the AI gold rush, drives their value sky-high.
The Case for Strategic Autonomy
Even so, should Europe ignore Huang’s warnings? Not entirely. At the very least, it would be prudent for Europe to ensure it can meet rising demand for AI applications domestically — even if that means relying on U.S.-based cloud services and chips.
Klein’s viewpoint aligns with the broader debate over Europe’s digital sovereignty. Earlier this year, he called plans to build European cloud infrastructure to compete with U.S. hyperscalers “nonsensical,” citing high energy costs that make such ventures economically unattractive. That challenge still looms, even as Europe aspires to take a leading role in AI.
In short, Klein’s argument is not against AI — it’s about being smart with how Europe invests in it. Rather than duplicating U.S.-style infrastructure, he believes the continent should play to its strengths, channeling funds into real-world applications that offer immediate and strategic value.
At SAP Sapphire 2025, SAP unveiled a major step forward in its sustainability ambitions, launching a suite of AI-driven tools for ESG management, carbon reporting, and compliance. These new solutions aim to streamline environmental oversight for enterprises, embedding sustainability into the heart of business operations.
The German enterprise software giant introduced a new data unification platform, promising to simplify ESG compliance and carbon accounting across complex corporate structures. Announced on May 23 during SAP’s annual flagship event held across multiple global locations, these innovations are part of SAP’s broader strategy to elevate sustainability data to the same level of importance as financial and operational metrics.
AI-Powered Compliance: From Paperwork to Proactive Insights
Set for beta release in August 2025, SAP’s enhanced Business AI capabilities will support a range of applications in environmental, health, and safety (EHS) as well as product compliance. These tools aim to reduce manual effort, accelerate processes, and improve accuracy.
One standout feature is the AI-powered permit management functionality in SAP S/4HANA for EHS, which automatically extracts key information from regulatory documents and suggests follow-up actions—essentially acting as a digital advisor for sustainability professionals.
Other enhancements include:
Conversational Safety Reporting: With the help of Joule, SAP’s AI copilot, employees can now submit incident reports using a chat-based interface, speeding up health and safety workflows.
Smart Safety Instruction Generator: AI analyzes risk assessments to suggest relevant safety measures.
Automated Product Compliance: AI extracts and maps data from certifications and safety sheets, minimizing errors and boosting efficiency.
These innovations are being bundled into SAP’s new SCM premium package, reflecting a growing focus on embedding AI into everyday business processes.
Real-World Applications: AI in Action
SAP’s AI tools are already supporting customers in real-world sustainability use cases:
Sustainability Control Tower: Helps streamline ESG reporting with editable templates, generative text, and data visualizations.
Sustainability Footprint Management: Uses AI to automate emissions mapping, matching products to lifecycle data with confidence scoring.
SAP Green Token: Automates validation of supplier declarations (such as ISCC certifications), giving businesses clear visibility into the sustainability of their supply chains.
According to SAP Chief Sustainability Officer Sophia Mendelsohn, businesses that fail to integrate sustainability into their AI initiatives risk falling behind. “Sustainability is emerging as one of the most impactful enterprise applications for AI,” she said.
What’s Coming Next: The Roadmap for 2025
Later this year, SAP plans to integrate its Sustainability Control Tower into the SAP Business Data Cloud, transforming it into an Intelligent Application that unifies operational and sustainability data on a single platform. This integration aims to give companies consistent, enterprise-wide reporting and decision-making capabilities.
Other upcoming releases include:
Structured emissions data (air, water, wastewater) from SAP EHS and S/4HANA.
Expanded datasets available through Sustainability Footprint Management for cloud users.
Early access previews for selected customers ahead of general availability.
Bridging Strategy and Execution with AI
SAP’s 2025 announcements reflect a strategic pivot—moving beyond tools and dashboards to embed sustainability into core operations. Gunther Rothermel, Co-GM and Chief Product Officer at SAP Sustainability, emphasized the shift: “These changes go well beyond technical updates. They represent a strategic shift: scaling sustainability within the core of business operations, powered by AI.”
SAP’s ultimate goal is to turn sustainability data into “decision-grade” intelligence—on par with financial reporting. Whether these new AI tools can close the execution gap many companies face in their ESG efforts will depend on adoption and outcomes. But with these launches, SAP has clearly positioned itself as a frontrunner in the next generation of enterprise sustainability solutions.